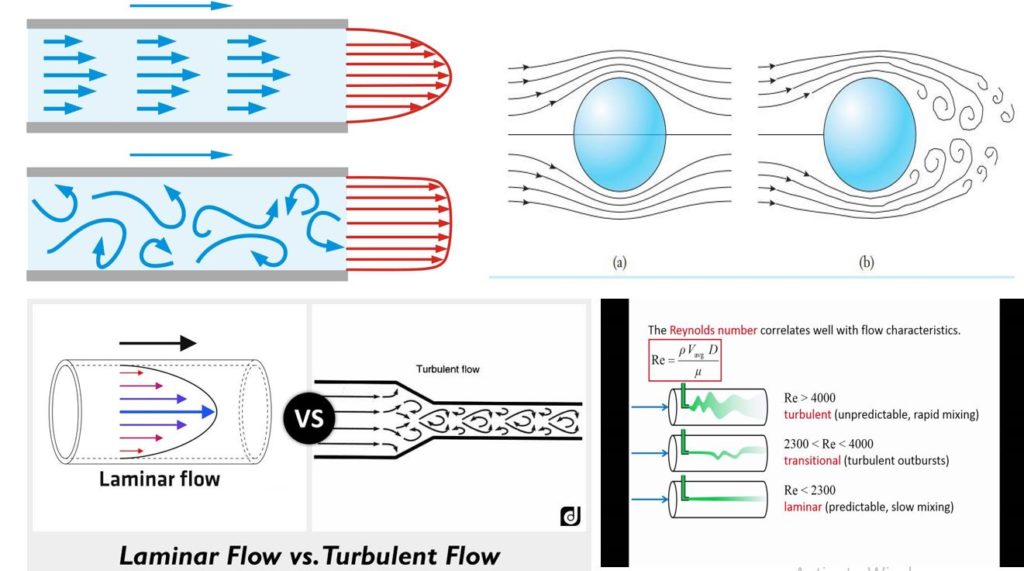
Question : What are the major difference between laminar Flow vs turbulent flow?
In fluid flows, there are two distinct fluid behaviors experimentally observed. These behaviors were first observed by Sir Osborne Reynolds.We will discuss this in detail in this article.
Laminar Flow: the flow of a fluid when each particle of the fluid follows a smooth path, paths which never interfere with one another. One result of laminar flow is that the velocity of the fluid is constant at any point in the fluid.
- The fluid flow in which the adjacent layers of the fluid do not mix with each other and moves parallel to each other, is called laminar flow.
- In the laminar flow, the fluid layer moves in straight line or considered to be moving in layers or laminae.
- The laminar flow always occurs when the fluid flow with low velocity and in small diameter pipes and the flow appears to be smooth without any mixing on a macroscopic scale between adjacent layers, even though mixing on molecular scale may exist.
- Reynolds number is used as a criterion for characterizing the flow as laminar or turbulent.
- The fluid flow having Reynolds number less than 2000 is called laminar flow.
- The fluid flow is very orderly i.e. there is no mixing of adjacent layers of the fluid and they move parallel to each other and also with the walls of the pipe.
- Shear stress in laminar flow depends only on the viscosity of the fluid and independent of the density.
Examples :
- A common example of laminar flow is the flow of honey or thick syrup from a bottle.
- For flow through pipes and ducts, the flow is generally considered to be laminar if the Reynolds number is less than 2300
Read also : Design of A Centrifugal Pump
Read Also : Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design
Turbulent Flow :
Irregular flow that is characterized by tiny whirlpool regions. The velocity of this fluid is definitely not constant at every point.
- Turbulent flows are characterized by a mixing action throughout the flow field caused by eddies in the flow.
- The fluid flow in which the adjacent layers of the fluid cross each other and do not move parallel to each other.
- In turbulent flow the fluid layers do not moves in straight line. They move randomly in zigzag manner.
- The turbulent flow occurs when the velocity of the fluid is high and it flows through larger diameter pipes.
- The fluid flow having Reynolds number greater than 4000 is called turbulent flow.
- The fluid does not flow in definite order. There is a mixing of different layers and they do not move parallel to each other but crosses each other.
- The shear stress in turbulent flow depends upon its density.
Examples of laminar and turbulent flow
- Blood flow in arteries,
- Oil transport in pipelines,
- Lava flow, atmosphere and ocean currents,
- flow through pumps and turbines, and
- Flow in boat wakes and around aircraft-wing tips. etc.
The difference is summarized in table below.
For better explanation watch the video given below: Laminar flow vs Turbulent flow
Hope,you got a clear picture of the difference between the two types of flow. Share this article with your friends.
ImageSource : Mechanical Engineering; GUNT – Equipment for engineering education; DifferenceBtw.com; YouTube
