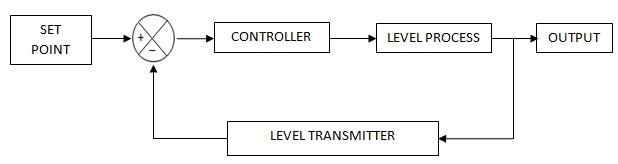
The increase/decrease height of the liquid level in a process vessel / tank depends upon the inlet and outlet flow rate of the processing fluid. If any imbalance in the inlet/outlet flow rates occurs, results a corresponding change into the height of the liquid level (which falls under control objective). Here our purpose is to maintain a desired height of the process fluid. In respect of that a level transmitter is placed which measures the ΔH (Height maximum – Height minimum); respectively by comparative study between the measured output and fixed set point, and the error (difference between set point and measured output) signal transferred to the controller, as a resultant as per the deviation from the set point, Action taken by the controller and regulates Final control element (Here by flow control valve’s in the output stream, %opening / %closing) to achieve a desired height.
Control Objective :
In order to develop a complete control strategy for this control loop, it is very important to identify the process variables first or one have to identify first what is controlled variables, what is manipulated variables and what falls under disturbance variables list.
Here the height of process fluid (H) is considered as controlled variable, which is your desired output.
Manipulated Variable : Outlet flow rate -controlled by control valve; as more fluid passes / flow rate increases from outlet valve height of liquid level decreases in the process vessel / tank and vice-versa . Here, outlet fluid flow rate is considered as manipulated variable. The fluid flow rate depends upon pump speed and all.
Major disturbances : Those parameters which affects the process fluid height:
- the flow rate of upstream/inlet processing fluid.
Control Action :
- In this loop reverse action controller is required, assuming a signal-to-regulate control valve:
- Here feed forward scheme is required, whenever any change in the height of the liquid occurs.
- In case of feed forward, what ever the disturbances occurs that gets accounted ( Here by means of level transmitter measures the height variation, including disturbance effects) and a comparison done between set point and measured output, whatever the error is their—–on that controller takes necessary action, give message to the flow transmitter and accordingly flow rate control valve, % open / %close taking place. In this way inlet/outlet flow rate increases/decreases or, decrease/increase responsible for level control of the tank.
Note :
- Continuous liquid level sensors are mainly get used in process industries which continuously measures liquid level of an entire system and keeps fluid level within a range.
ImageSource : Control Notes ;
Also Read:
Piping and Instrumentation Diagram – P&ID
How to choose betwwen PLC and DCS systems for process industries ?
Cement Manufacturing Process
Vinyl Chloride from Ethylene
Cooling Tower
Psychrometric Chart
What is Boiler ?
Venturi Flow Meter
Pitot Tube
Coriolis Mass Flow Meter
RECIPROCATING PUMP
Design of Centrifugal Pump
Valve & Its Types
Cavitation
P&ID Symbols and Notation
What is the Difference Between HMI and SCADA?
What is SCADA ? How does SCADA Works?
What is Programmable Logic Controller / PLC ?
