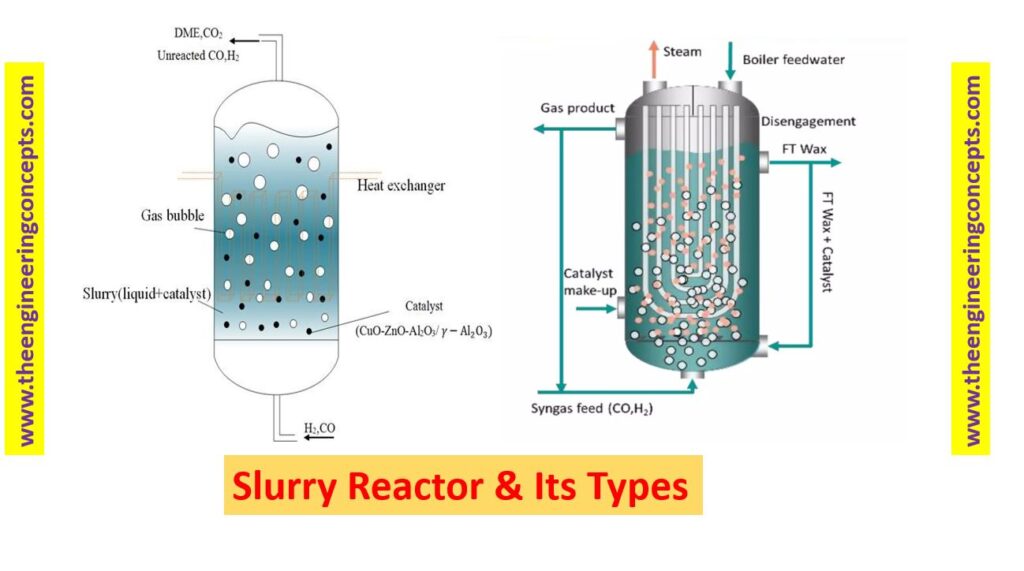
In a slurry reactor, the solid particles are typically finely divided and can be catalysts, precursors, or reactants themselves. The liquid medium acts as a solvent or a carrier for the reactants and enables the transport of heat and mass. The reactants are mixed with the solid particles and the liquid medium, forming a heterogeneous mixture. The slurry is continuously circulated through the reactor to maintain the desired reaction conditions. There are several advantages of using a slurry reactor:
- Enhanced reaction kinetics: The use of a slurry allows for increased surface area contact between the reactants and the solid catalyst, leading to improved reaction rates. The fine particle size and uniform mixing in the slurry promote efficient mass transfer and ensure a high degree of contact between the reactants and the catalyst.
- Heat transfer efficiency: The liquid medium in the slurry acts as a heat transfer medium, facilitating the dissipation of heat generated during the reaction. The efficient heat transfer helps in maintaining the desired reaction temperature, preventing temperature gradients and hotspots.
- Mass transfer efficiency: The slurry configuration enables effective mass transfer between the reactants, catalyst, and liquid medium. The liquid phase provides a medium for the diffusion of reactants and products, allowing for better mixing and distribution of species, and enhancing overall mass transfer rates.
- Flexibility in catalyst loading: Slurry reactors provide flexibility in catalyst loading, allowing for the use of higher catalyst concentrations compared to fixed-bed reactors. This can lead to improved catalyst utilization and overall reactor performance.
However, there are also challenges associated with slurry reactors, including:
- Separation of solid and liquid phases: After the reaction, separating the solid catalyst from the liquid products can be challenging. Solid-liquid separation techniques such as filtration or centrifugation are typically employed to recover the catalyst and obtain the desired product.
- Potential for catalyst deactivation: The presence of solid particles in the slurry can lead to catalyst fouling, poisoning, or deactivation over time. These issues may require additional steps such as catalyst regeneration or replacement.
Types of Slurry Reactor:
- Slurry Bubble Column Reactor:
- In a slurry bubble column reactor, to achieve the best possible gas exchange, gas is injected towards the bottom of the column to create a turbulent stream. There are a variety of building materials available in the industry. Though, gas sparging is used to combine materials as it uses less energy than mechanical stirring. Here, the liquid may flow in parallel or in the counter-current direction.