Vortex flow meter
Vortex flowmeters are used to measure pressure in the pipeline, creating vortices in the flow channel using a stationary object (Bluff body). The vortex flowmeters are used for measuring gases and liquids in pipeline flowing full.
Principle:
Vortex flowmeters make use of a principle called the Theodore von Karman’s effect.
According to this principle, flow will alternately generate vortices when passing by a bluff body. A bluff body has a broad, flat front. In a vortex meter, the bluff body is a piece of material with a broad, flat front that extends vertically into the flowstream. Flow velocity is proportional to the frequency of the vortices. Flowrate is calculated by multiplying the area of the pipe times the velocity of the flow.
In some cases, vortex meters require the use of straightening vanes or straight upstream piping to eliminate distorted flow patterns and swirl. Low flowrates present a problem for vortex meters, because they generate vortices irregularly under low flow conditions. The accuracy of vortex meters is from medium to high, depending on model and manufacturer. In addition to liquid and gas flow measurement, vortex flowmeters are widely used to measure steam flow.
It was determined that the distance between successive vortices downstream of the stationary object is relatively constant, and directly proportional to the width of the object, for a wide range of Reynolds number values.
f=(St*V)/d
f = vortex frequency
St = Strouhal’s number dimensionless
V = medium flow rate
d = the width of triangle prim
Working:
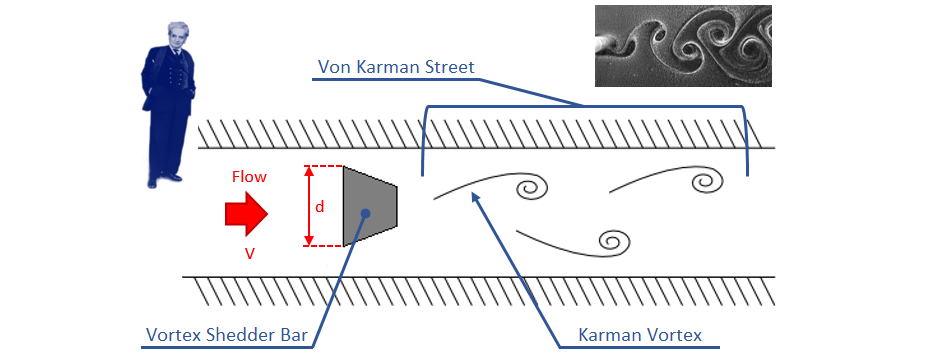
- Triangle shaped bluff body is fixed at the centre of the pipeline.
- Vortices are formed continuously in the stream because of the bluff body. The vortices fade as it moves away from the Bluff body.
- The vortices formed at either side of the bluff body are alternate to each other. So that, there is a pressure difference on either side.
- These pressure difference is measured continuously by sensor tubes installed on either side. The fluctuation of pressure is measured and converted to an alternating signal as an output.
- The frequency of the alternating signal produced is proportional to the frequency of the vortices produced. The frequency of the vortices is directionally proportional to the flow.
Advantages of Vortex flowmeter:
- Extremely versatile : Can be used for Gas, liquid and steam
- Low wear
- Have no moving parts
- Low cost for installation and maintanence
- Wide range ability
- Inherently linear output
- Immune to density and viscosity changes
- Applicable to wide range of process temperature
Disadvantages of Vortex flowmeter:
- Works over a particular velocity range
- Not suitable very low flow rates
- Requires specialization for different fluid flow measurement
- May cause presssure drop due to presence of bluff body
ImageSource :
Yokogawa ;
Emerson ;
Sierra Instruments
ArticleSource : Flow Control Network